Tracking Tectonic Activity: Earthquake Monitoring in Anchorage
Anchorage, Alaska, is a city that sits on the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area known for its seismic activity. The region’s geological features make it one of the most earthquake-prone places in the world. Understanding and monitoring tectonic activity is essential for ensuring public safety, infrastructure integrity, and disaster preparedness. This article explores the mechanisms behind earthquake monitoring in Anchorage, technologies used, significant historical earthquakes, and the future of seismic safety in the region.
The Geological Background of Anchorage

Anchorage is located at the convergence of two major tectonic plates: the North American Plate and the Pacific Plate. This juxtaposition creates a complex geological environment characterized by frequent earthquakes. Key features of this area include:
- Subduction Zones: The Pacific Plate is constantly being forced under the North American Plate, creating immense pressure.
- Fault Lines: The area is crisscrossed with numerous fault lines, including the well-known Denali Fault.
- Volcanic Activity: The tectonic dynamics also contribute to volcanic activity in the surrounding regions.
These geological characteristics make Anchorage both a fascinating study area and a location of significant risk concerning earthquakes.
The Importance of Earthquake Monitoring
Monitoring tectonic activity is crucial for several reasons:
- Public Safety: Timely alerts can save lives by warning residents before an earthquake strikes.
- Infrastructure Integrity: Continuous monitoring helps assess and reinforce buildings and roads to withstand seismic forces.
- Scientific Research: Data collected contributes to a broader understanding of seismic activity globally.
In Anchorage, the local government and various organizations invest heavily in earthquake monitoring systems to mitigate risks associated with seismic events.
Technologies Used in Earthquake Monitoring
Anchorage utilizes a variety of advanced technologies to monitor seismic activity effectively:
- Seismographs: These devices measure ground motion and provide real-time data on earthquakes.
- GPS Stations: Global Positioning System technology helps track the slow movements of tectonic plates.
- ShakeMaps: These maps illustrate the intensity and impact of earthquakes in real-time, helping responders assess the situation.
- Early Warning Systems: Systems like ShakeAlert provide alerts seconds before seismic waves reach populated areas.
These tools work in tandem to create a comprehensive monitoring network that aims to predict and respond to earthquakes effectively.
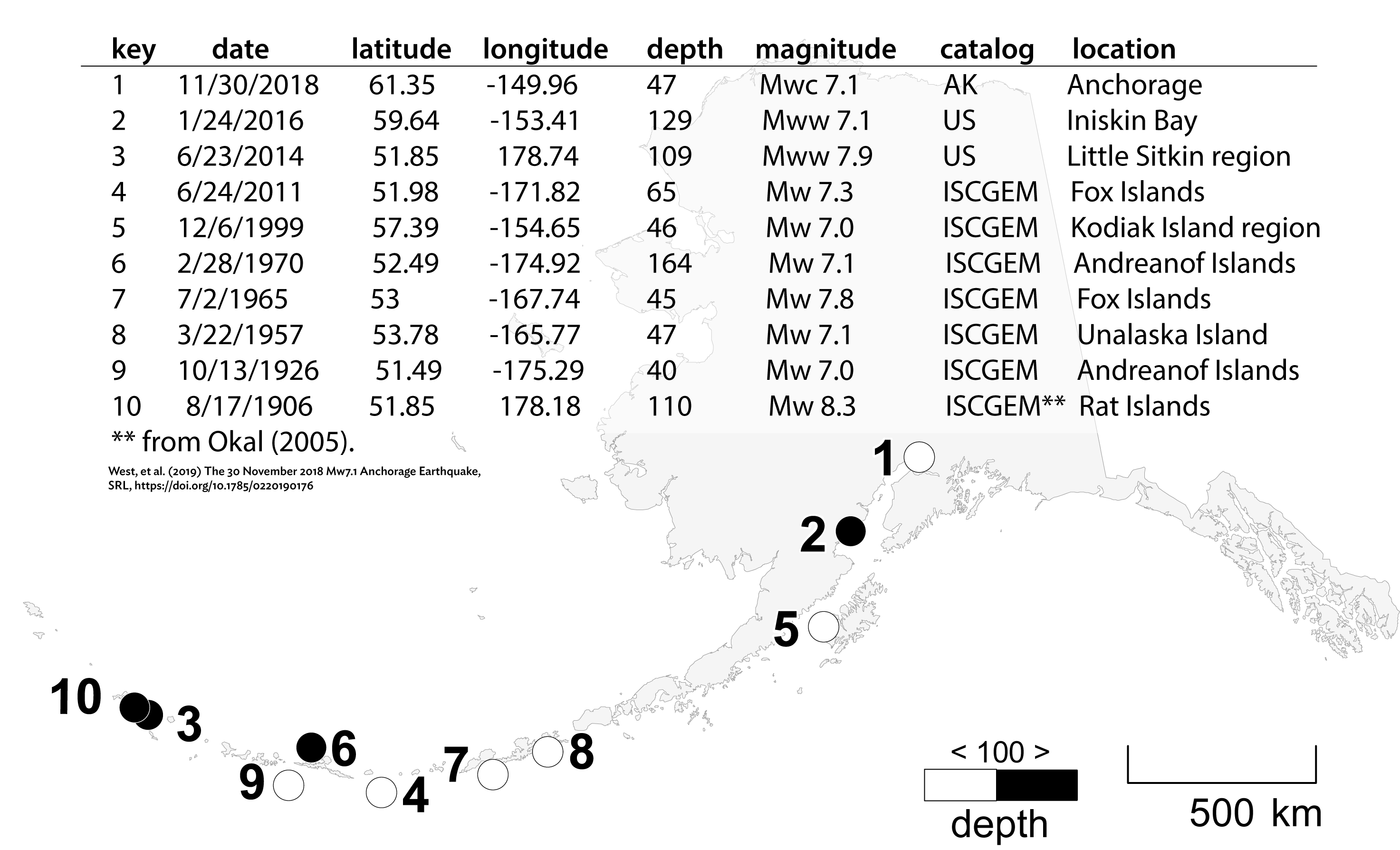
Significant Earthquakes in Anchorage History
Anchorage has experienced several significant earthquakes that have shaped its approach to seismic monitoring:
- 1964 Great Alaska Earthquake: This 9.2 magnitude earthquake remains the most powerful recorded in North America. It caused massive destruction and is a pivotal event in Alaskan seismic history.
- 2001 Earthquake: A magnitude 7.0 quake struck near the city, leading to extensive monitoring and public education efforts.
- 2018 Anchorage Earthquake: A 7.0 magnitude quake caused substantial damage but also demonstrated the effectiveness of the city’s monitoring systems, as alerts were sent out promptly.
These events have underscored the need for continual advancements in monitoring technology and public safety measures.
Case Study: The 1964 Great Alaska Earthquake
The 1964 earthquake serves as a critical case study in understanding the impact of seismic events. This event resulted in:
- Approximately 131 deaths.
- Significant property damage estimated at $311 million (equivalent to over $2 billion today).
- Triggered tsunamis that affected coastal towns across the Pacific, reaching as far as Hawaii and California.
The aftermath of this earthquake led to significant changes in building codes, emergency preparedness, and the establishment of robust earthquake monitoring systems in Alaska.
Community Preparedness and Education
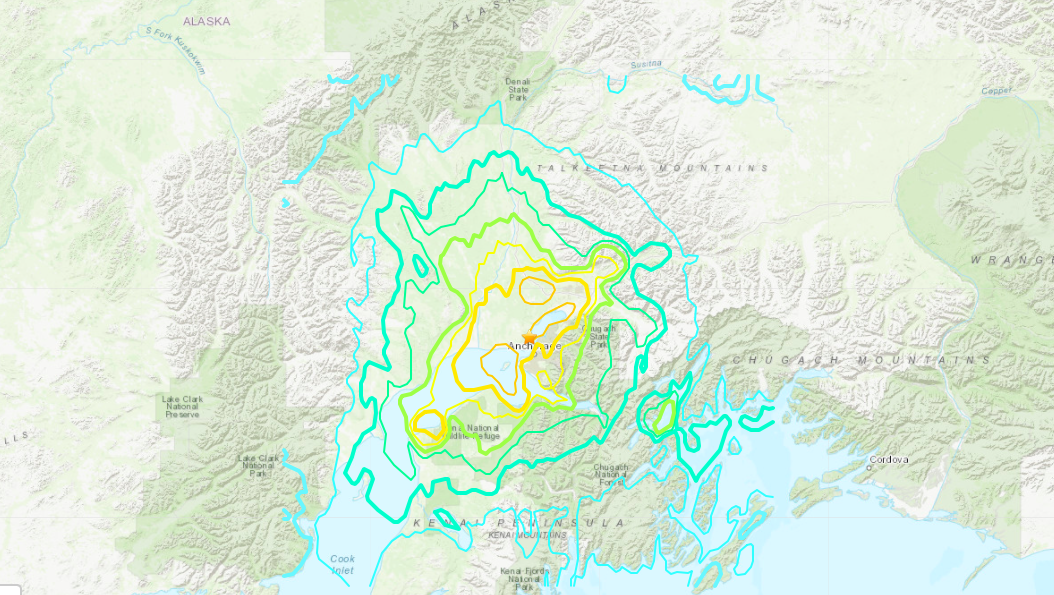
Anchorage has made substantial advances in community preparedness regarding earthquakes. Educational programs include:
- Drills and Training: Regular earthquake drills are conducted in schools, workplaces, and communities.
- Public Education Campaigns: Initiatives to educate residents about earthquake safety, including how to “Drop, Cover, and Hold On.”
- Emergency Kits: Encouragement for households to maintain emergency kits and plans.
These efforts aim to empower residents to respond effectively in the event of an earthquake, thereby reducing potential casualties.
The Future of Earthquake Monitoring in Anchorage

As technology continues to evolve, the future of earthquake monitoring in Anchorage looks promising:
- Artificial Intelligence: The use of AI to analyze seismic data could lead to better predictive models.
- Improved Infrastructure: Smart technologies in buildings can enhance resilience against earthquakes.
- Community Engagement: Increased involvement of local communities in preparedness initiatives.
The integration of these advancements holds the potential to further improve the safety and preparedness of Anchorage residents.
Monitoring tectonic activity and earthquake preparedness in Anchorage is a multifaceted endeavor that blends technology, community involvement, and historical context. The unique geological features of this region demand a robust response to the inherent risks posed by earthquakes. Through advanced technologies, public education, and ongoing research, Anchorage is better equipped than ever to face the seismic challenges of the future. By learning from past events and investing in modern solutions, the city aims to protect its residents and infrastructure from the unpredictable nature of tectonic activity.


